TSIII SA implant installation accompanying sinus lift with lateral approach; a case report
Authors: Gi-Young Seo, Jae-Kook Cha, Jae-Hong Lee, Jung-Seok Lee, Ui-Won Jung, Seong-Ho Choi, Kyoo-Sung Cho, Jung-Kiu Chai, Chang-Sung Kim
Goal
Loss of maxillary molar teeth leads to rapid resorption of bone in the alveolar process below the maxillary sinus floor. The sinus floor augmentation procedure is one of the most predictable grafting procedures available for placing dental implants in the severely atrophic posterior maxilla. Sinus augmentation is classified according to residual alveolar bone height. When the residual bone height is 3~4 mm, 1-step lateral approach is recommended. This clinical case report presents patient subjected to a maxillary sinus lift (Lateral approach) and immediate implant placement (TSIII ) with synthetic bone grafting.
Materials & Methods
Right maxillary molar and premolar teeth (Teeth number 17, 16, 15, 14) were missing state. In pre-surgical computed tomographic scan images, residual bone height was about 3.3 mm. First stage implant surgery was performed using TSIII with sinus lift. Lateral approach for the open-window method using round bur and for sinus lifting with placement of alloplast (Osteon II ) was carried out. Second stage surgery was performed after 4 months of healing.
Results
Sinus augmentation with simultaneous implantation (1-step lateral approach) was a predictable technique with low surgical morbidity that allows shorter healing times in patient with reduced bone height.
Conclusion
There were no surgical complications such as sinus membrane perforation. Achieving initial implant stability and maintaining parallelism are major concerns in implant placement, especially when implants are placed in less than 5 mm of bone. The case report demonstrates that TSIII implant installation on augmented ridge showed competent initial stability (30N). In addition, periotest value (PTV=-6.8) measured during second surgery reflected successful osteointegration.
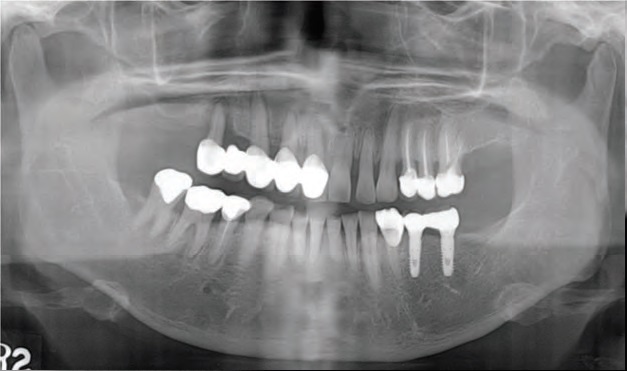
Fig. 1. Pre-operative panoramic view.
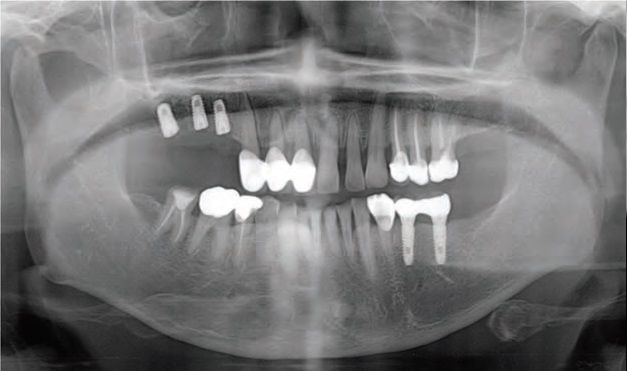
Fig. 2. Implant fixture installation on panoramic view.
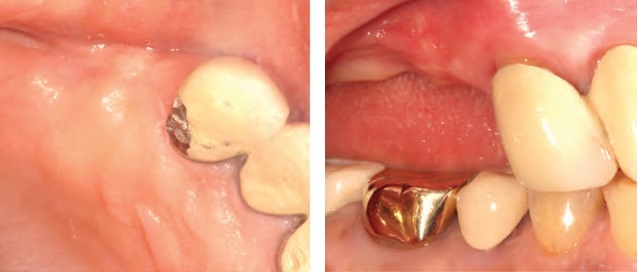
Fig. 3. Pre-operative clinical photo. left: Occlusal view. right: Lateral view.
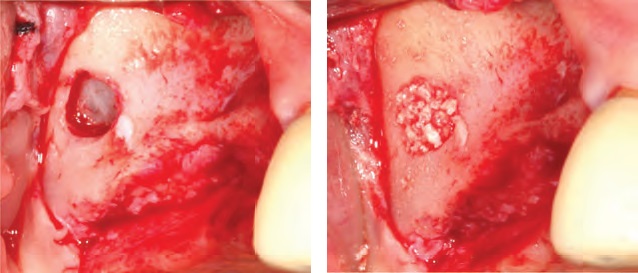
Fig. 4. Sinus lift with lateral approach. left: Right sinus window opening. right: Bone grafting
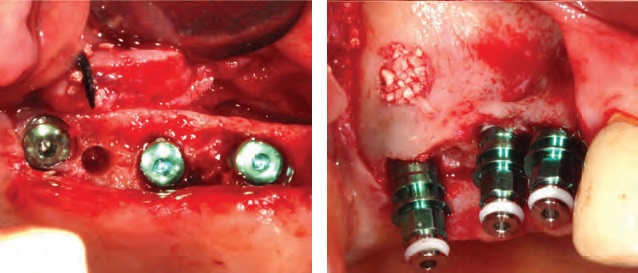
Fig. 5. TSIII Implant installation. left: Occlusal view. right: Lateral view.
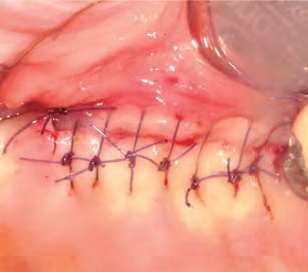
Fig. 6. Suture
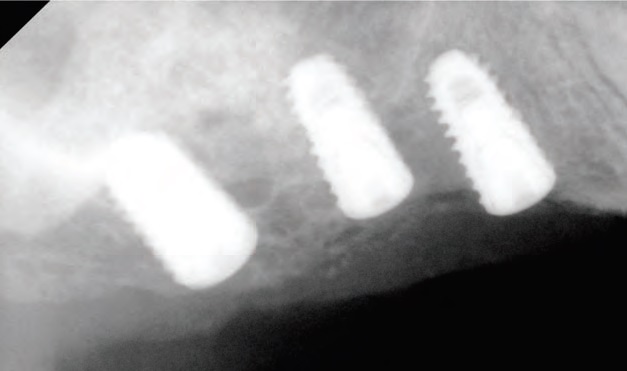
Fig. 7. Implant installation on peri-apical X-ray view.
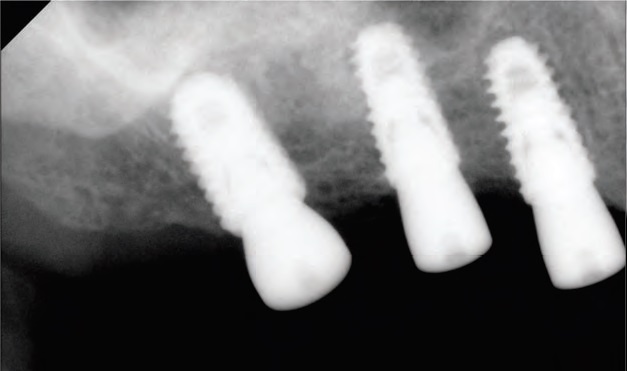
Fig. 8. Second stage surgery after 4 months.