Evaluation of Biomechanical Effect TS System Pre-Clinical Study on Chemically Modified CA Surface in Vivo
Authors: Jeong Jong Cheol
Goal
The aim of the study was to evaluate the effect of chemically modified hydrophilic CA surface compared with conventional SA surface in various animals.
Materials & Methods
A total of 20 implants were divided into two groups. Group 1, implants treated with SA were used as control group. Group 2 retained chemically modified hydrophilic CA surface. All implants were placed in the tibiae of 3 female New Zealand white rabbits and in the mandible of 2 male miniature pigs. Removal torque was measured 16days after placement.
Results
In tibiae of rabbit, group 1 had a mean removal torque of 50 Ncm versus 72 Ncm for group 2 after 16days of healing time. In mandible of miniature pig, group 1 had a mean removal torque of 68 Ncm versus 75 Ncm for group 2 after 2 weeks of healing time. Group 2 was measured more stable anchorage than group 1 in both animals.
Conclusion
It is concluded that modified hydrophilic CA sufaces were more effective for bio mechanical properties of bone implant contact from conventional SA surface in rabbits and miniature pigs.
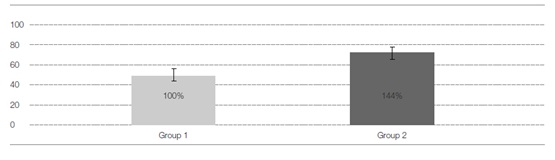
Fig. 1. The result of Removal torque in tibia of rabbits. Group 2 increased more than 40% of mean value compared with group. The sample size for group was 5.
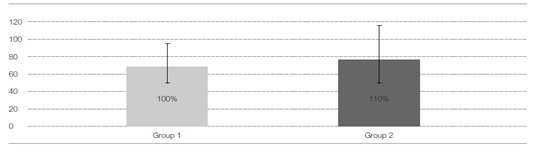
Fig. 2. The result of Removal torque in mandible of miniature pigs. Group 2 increased more than 10% of mean value compared with group. The sample size for group was 10.